What is Apple Music Spatial Audio?
First, let’s take a look at Spatial Audio and what it means for your listening enjoyment. With Spatial Audio, you’ll hear supported Apple Music titles coming from all directions from your supported devices. Think about the multiple sounds you hear at the cinema, and that’s basically the concept behind Spatial Audio, except, in this case, the sound moves with you as the position of your device changes. To succeed, Spatial Audio relies on gyroscopes and sensors on the devices. Initially launched only for video, Spatial Audio on Apple Music is supported on all AirPods and Beats headphones, including an Apple H1 or WI chip. Additionally, it works with the built-in speakers in the newest iPhone, iPad, and Mac versions. It’s also worth noting that Microsoft has Spatial Audio on Windows 10 built-in. For more on that read our article on how to turn on Windows Sonic Spatial Sound in Windows 10.
What About Dolby Atmos?
Dolby Atmos is similar to Spatial Audio and allows film and music creators to designate where sounds are coming from and the distance. With Dolby Atmos, a listener may hear content from up to 128 channels played on up to 34 separate speakers at the same time. Headphones, which have much fewer physical speakers than sound systems, can still support Dolby Atmos using unique mixing techniques. The result is a highly effective simulated 3D audio experience that features depth and direction. The supported Dolby Atmos systems list continues to grow and now includes computers, TV sets, and current-generation sound systems. Like Spatial Audio, it’s supported on Apple’s AirPods, Beats headphones, plus iPhone, iPad, and Mac.
Spatial Audio + Dolby Atmos
The best way to look at the difference between Spatial Audio and Dolby Atmos is like this: Dolby Atmos fixes front-channel audio to your head. By contrast, Spatial Audio fixes front-channel audio to your devices, such as an iPhone or iPad, with no regard to the position of your head. At least initially, you’re going to find more Dolby Atmos content on Apple Music than Spatial Audio. More adoption from artists, however, will change this so that most tracks will support both technologies.
Setting Up Spatial Audio With Dolby Atmos
There are different ways to set up and use Spatial Audio with Dolby Atmos on your Apple devices. You must also keep in mind that supported devices such as iPhone only work when using built-in speakers or supported headphones.
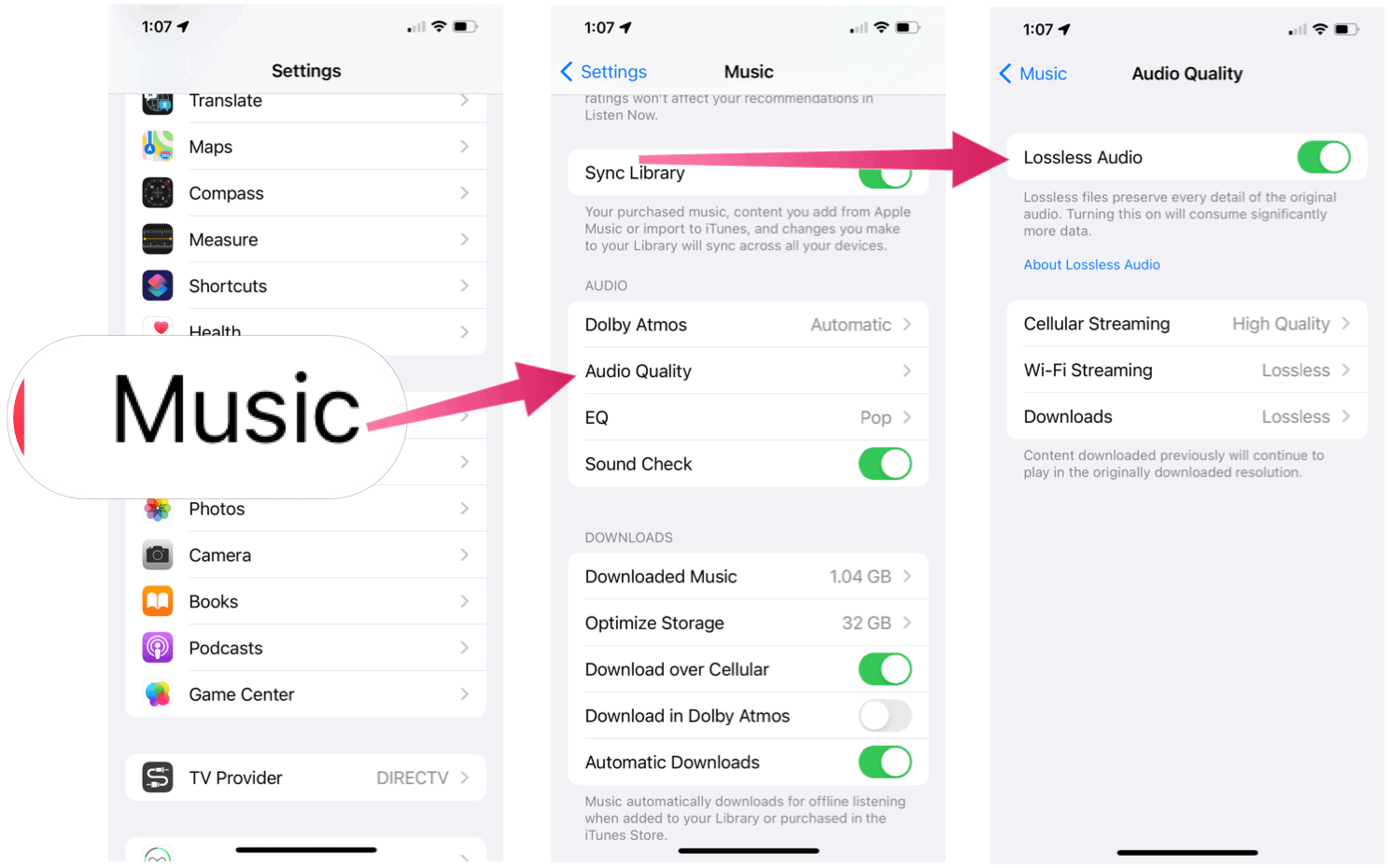
iPhone / iPad
Here’s what you need to do to get started with Spatial Audio With Dolby Atmos on iPhone or iPad:
To turn Lossless Audio on/off:
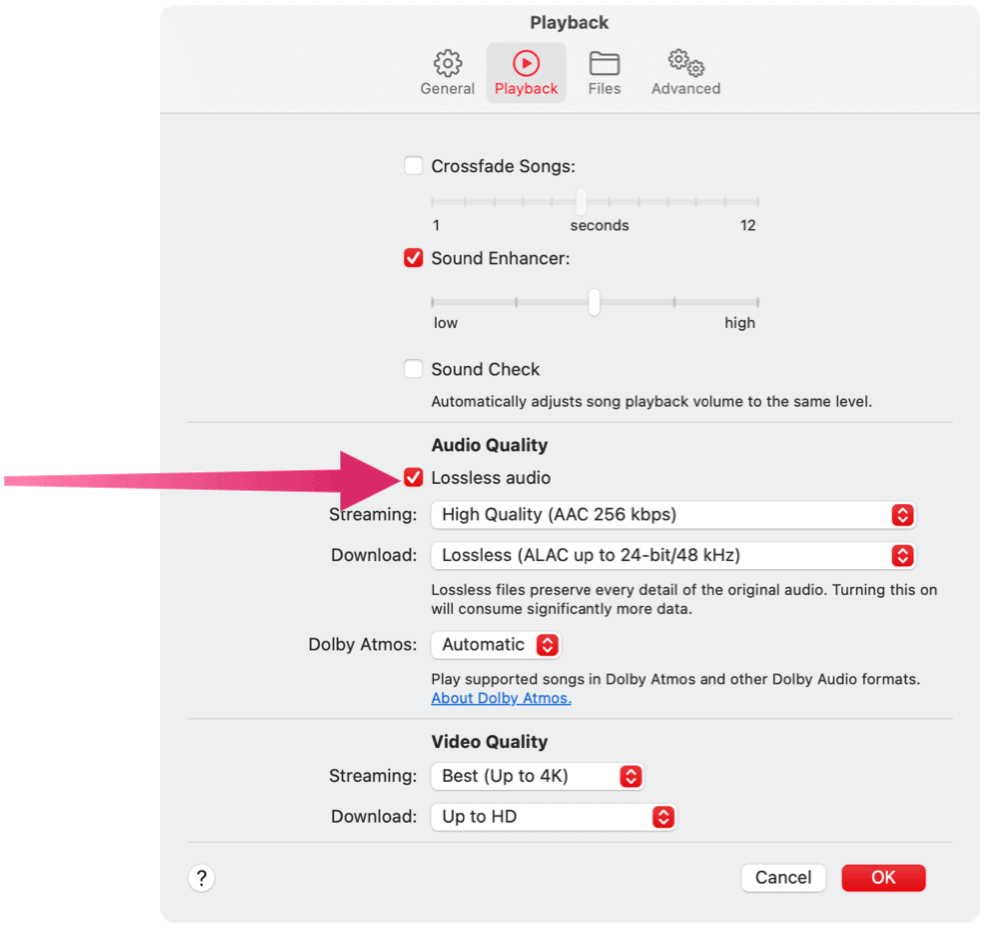
Mac
On macOS, do the following to use Spatial Audio with Dolby Atmos:
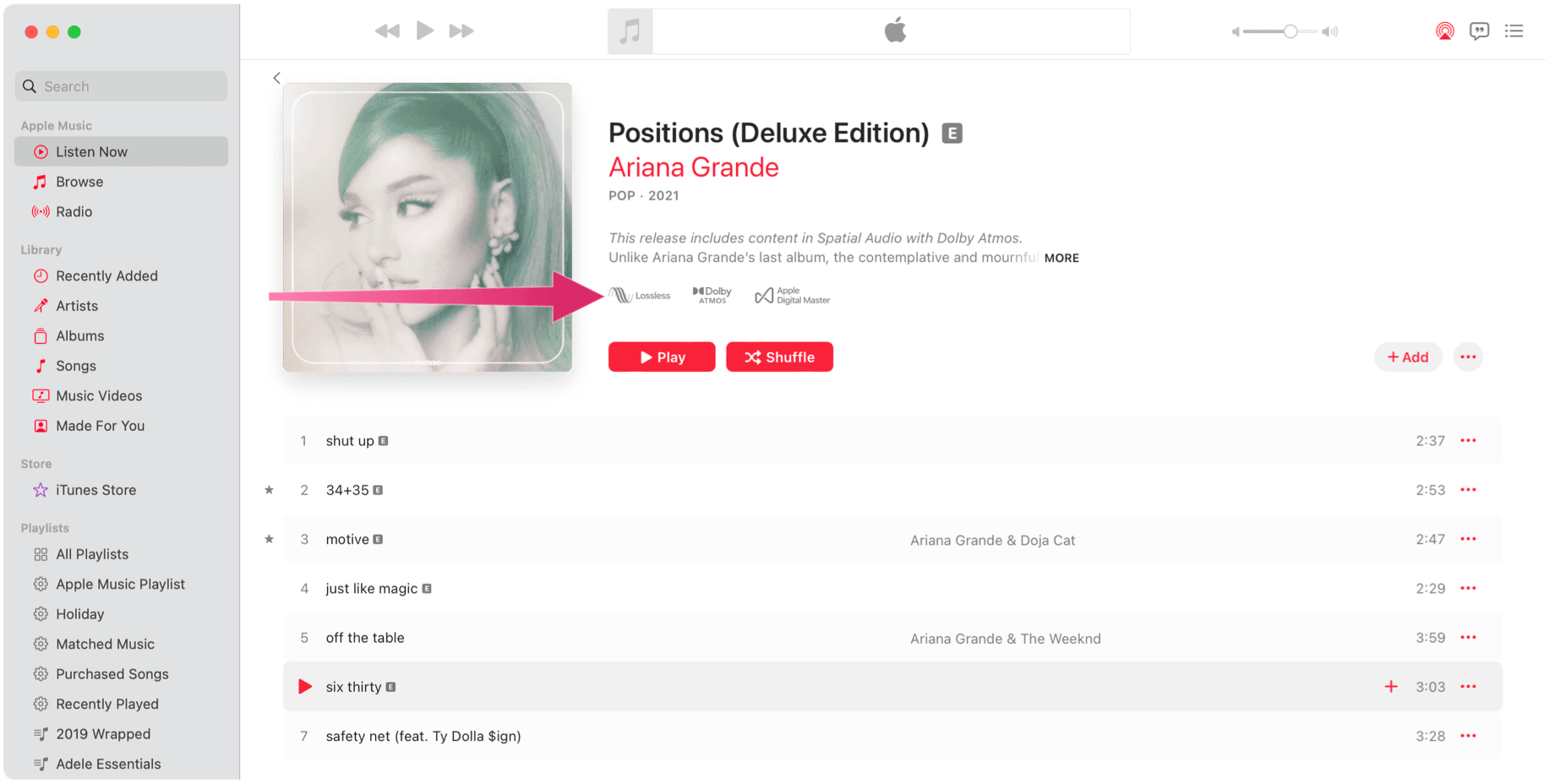
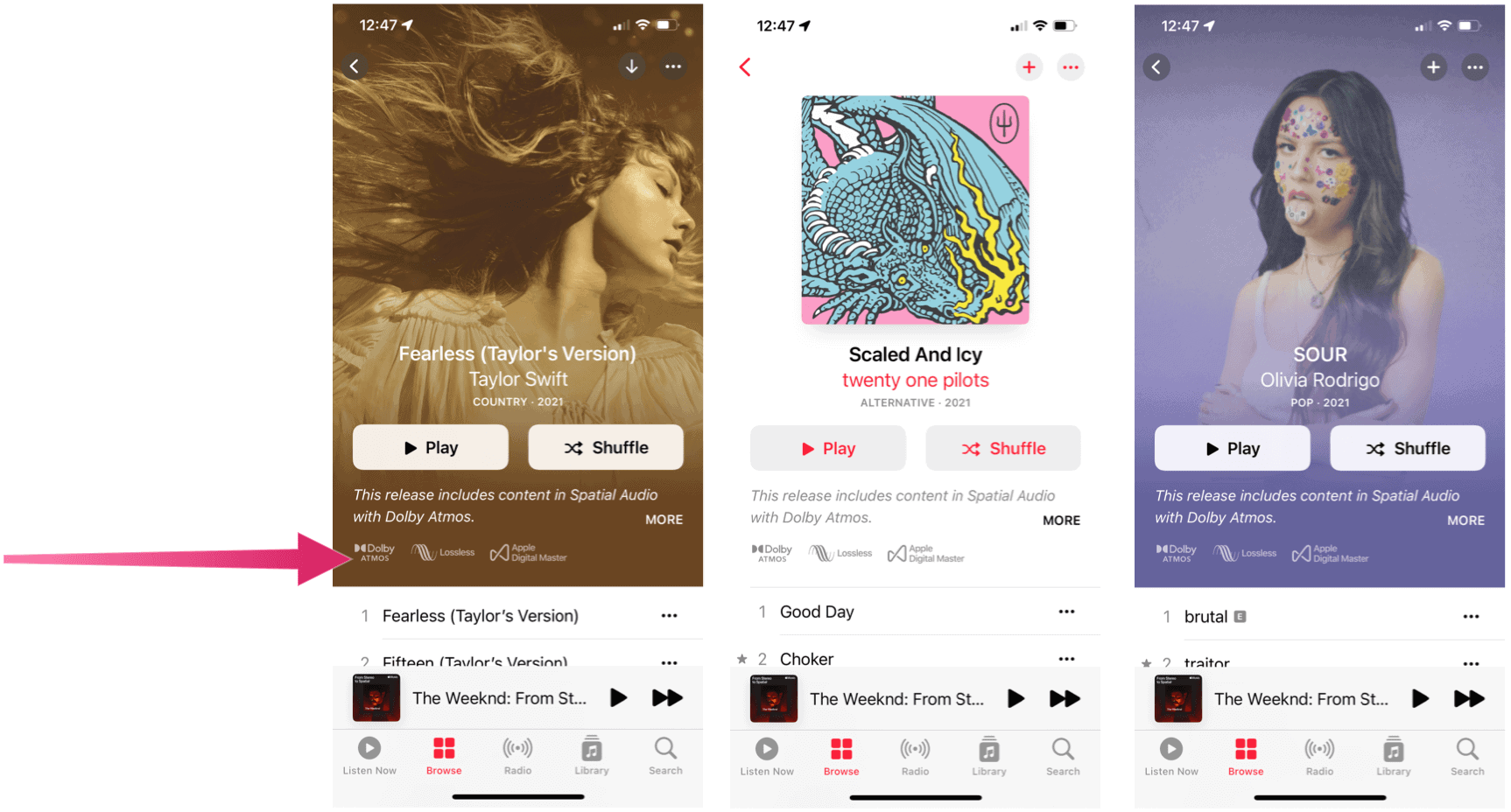
Is a Track or Album Supported?
Content that supports Apple Music Spatial Audio with Dolby Atmos is marked as such, regardless of the platform, as you can see in the examples below.
Requirements
Even if a track supports Lossless Audio, as does your device, you might not actually hear it in the format. That’s because the requirements are much steeper than Apple Music Spatial Audio with Dolby Atmos. As Apple explains:
iOS/iPadOS 14.6 or later installed on your device.The built-in speakers.To listen to songs at sample rates higher than 48 kHz, you need an external digital-to-analog converter.
To turn Lossless Audio on/off: You can now select the audio quality for Cellular, Wi-Fi streaming, and Downloads. The choices for Lossless Audio include:
Lossless for a maximum resolution of 24-bit/48 kHz.Hi-Res Lossless for a maximum resolution of 24-bit/192 kHz.
As noted above, Lossless Audio over a cellular or Wi-Fi network consumes significantly more data. Additionally, downloaded Lossless Audio files use much more space on your device, with higher resolutions using more data than lower ones. Watch you don’t go over your cellular limits.
Mac
To listen to Lossless Audio on your Mac, you must have:
macOS 11.4 or later installed on your device.A wired connection to headphones, receivers, or powered speakers.The built-in speakers.To listen to songs at sample rates higher than 48 kHz, you need an external digital-to-analog converter.
The choices include:
Lossless for a maximum resolution of 24-bit/48 kHz.Hi-Res Lossless for a maximum resolution of 24-bit/192 kHz.
Once again, Lossless Audio over a Wi-Fi network consumes significantly more data. Additionally, downloaded Lossless Audio files use much more space on your device, with higher resolutions using more data than lower ones.
Lossless Audio: Does It Matter?
While it’s great seeing Apple Music offer Lossless Audio (and without a price hike), you must be asking whether the requirements and large file sizes make it worth it. Perhaps, it’s best to read what Apple said on the subject: Cupertino’s decision to bring Spatial Audio with Dolby Atmos and Lossless Audio with no price hike for subscribers is a big deal for the consumers and the company alike. For users, having higher-quality music is obviously better. And for Apple, the new features make it less likely someone will ditch Apple Music for something else because of the natural compatibility between the music updates and hardware. Comment Name * Email *
Δ Save my name and email and send me emails as new comments are made to this post.
![]()